One of the most important concepts we teach in economics, and most importantly in macroeconomics, is the notion of the fallacy of composition.
Students and others who haven’t been exposed to macroeconomics naturally extrapolate from their own individual situation to society and the economy as a whole.
This often leads to the problem of the fallacy of composition. Of course, that isn’t just restricted to economics. While a few people could exit the doors of a crowded movie theatre, all of us could not.
The macroeconomics example of the fallacy of composition most often used is the paradox of thrift. Any individual can increase her saving by reducing her spending—on consumption goods. So long as her decision does not affect her income—and there is no reason to assume that it would—she ends up with less consumption and more saving.
The example I always use involves Mary who usually eats a hamburger at Macdonald’s every day. She decides to forego one hamburger per week, to accumulate savings. Of course, so long as she sticks to her plan, she will add to her savings (and financial wealth) every week.
The question is this: what if everyone did the same thing as Mary—would the reduction of the consumption of hamburgers raise aggregate (national) saving (and financial wealth)?
The answer is that it will not. Why not? Because Macdonald’s will not sell as many hamburgers, it will begin to lay-off workers and reduce its orders for bread, meat, catsup, pickles, and so on.
All those workers who lose their jobs will have lower incomes, and will have to reduce their own saving. You can use the notion of the multiplier to show that this process comes to a stop when the lower saving by all those who lost their jobs equals the higher saving of all those who cut their hamburger consumption. At the aggregate level, there is no accumulation of savings (financial wealth).
Of course that is a simple and even silly example. But the underlying explanation is that when we look at the individual’s increase of saving, we can safely ignore any macro effects because they are so small that they have only an infinitely small impact on the economy as a whole.
But if everyone tries to increase saving, we cannot ignore the effects of lower spending on the economy as a whole. That is the point that has to be driven home.
We can then again return to the notion of the multiplier, and show that the way to increase aggregate saving is by increasing spending, specifically, nonconsumption spending—spending on investment, spending by government, or spending by foreigners on our exports.
I don’t want to go into that particular example any further. Another example that is less frequently used concerns unemployment.
The view shared by most of my undergraduate students is that unemployment is caused by laziness or lack of training. The argument they often use is that “I can get a job, therefore all the unemployed could get jobs if only they tried harder, or got better education and training”.
The way I go about demonstrating that fallacy is a dogs and bones example. Say we have 10 dogs and we bury 9 bones in the backyard. We send the dogs out to find bones. At least one dog will come back without a bone.
We decide that the problem is lack of training. We put that dog through rigorous training in the latest bone finding techniques. We bury 9 bones and send the 10 dogs out again. The trained dog ends up with a bone, but some other dog comes back without a bone (empty-mouthed, so to speak).
The problem, of course, is that there are not enough bones and jobs to go around. It is certainly true that a well-trained and highly motivated jobseeker can usually find a job. But that is no evidence that aggregate unemployment is caused by laziness or lack of training.
We could also go into the common belief that minimum wages cause unemployment. It is at least partly true that for an individual firm, higher wages reduce the number of workers hired. But we cannot extrapolate that to the economy as a whole. Higher wages mean higher income and thus higher consumption spending, which induces firms to employ more labor. So the truth is that economic theory does not tell us that raising minimum wages will lead to more unemployment, indeed, theory tells us it can go the other way—raising the minimum wage could increase employment.
Again, the reason we can reach the wrong conclusion in all of these cases when we aggregate up from the micro level to the macro is because we ignore the impacts that behavior of individuals or firms has on other individuals or firms. That can be OK for the case of the individual firm or household, but is almost certainly incorrect for firms and households taken as a whole.
Let me move on to a more important fallacy of composition. We hear politicians and the media arguing that the current federal budget deficit is unsustainable. I have heard numerous politicians refer to their own household situation: if my household continually spent more than its income year after year, it would go bankrupt. Hence, the federal government is on a path to insolvency, and by implication, the budget deficit is bankrupting the nation.
That is another type of fallacy of composition. It ignores the impact that the budget deficit has on other sectors of the economy. Let me go through this in some detail, as it is more complicated than the other examples.
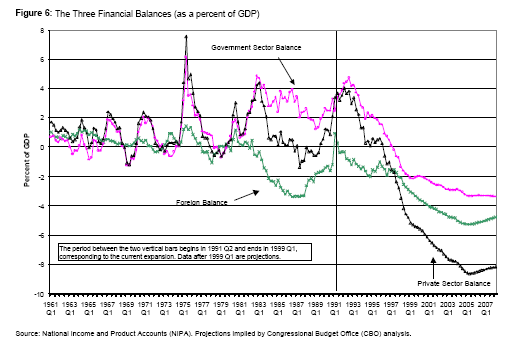
We can divide the economy into 3 sectors. Let’s keep this as simple as possible: there is a private sector that includes both households and firms. There is a government sector that includes both the federal government as well as all levels of state and local governments. And there is a foreign sector that includes imports and exports; (in the simplest model, we can summarize that as net exports—the difference between imports and exports—although to be entirely accurate, we use the current account balance as the measure of the impact of the foreign sector on the balance of income and spending).
At the aggregate level, the dollar spending of all three sectors combined must equal the income received by the three sectors combined. Aggregate spending equals aggregate income. But there is no reason why any one sector must spend an amount exactly equal to its income. One sector can run a surplus (spend less than its income) so long as another runs a deficit (spends more than its income).
Historically the US private sector spends less than its income—that is it runs a surplus. Another way of saying that is that the private sector saves. In the past, on average the private sector spent about 97 cents for every dollar of income.
Historically, the US on average ran a balanced current account—our imports were just about equal to our exports. (As discussed below, that has changed in recent years, so that today the US runs a huge current account deficit.)
Now, if the foreign sector is balanced and the private sector runs a surplus, this means by identity that the government sector runs a deficit. And, in fact, historically the government sector taken as a whole averaged a deficit: it spent about $1.03 for every dollar of national income.
Note that that budget deficit exactly offsets the private sector’s surplus—which was about 3 cents of every dollar of income. In fact, if we have a balanced foreign sector, there is no way for the private sector as a whole to save unless the government runs a deficit. Without a government deficit, there would be no private saving. Sure, one individual can spend less than her income, but another would have to spend more than his income.
While it is commonly believed that continual budget deficits will bankrupt the nation, in reality, those budget deficits are the only way that our private sector can save and accumulate net financial wealth.
Budget deficits represent private sector savings. Or another way of putting it: every time the government runs a deficit and issues a bond, adding to the financial wealth of the private sector. (Technically, the sum of the private sector surpluses equal the sum of the government sector deficits, which equals the outstanding government debt—so long as the foreign sector is balanced.)
Of course, the opposite would also be true. Assume we have a balanced foreign sector and that the government runs a surplus—meaning its tax revenues are greater than government spending. By identity this means the private sector is spending more than its income, in other words, it is deficit spending. The deficit spending means it is going into debt, and at the aggregate level it is reducing its net financial wealth.
At the same time, the government budget surplus means the government is reducing its debt. Effectively what happens is that the private sector returns government bonds to the government for retirement—the reduction of private sector wealth equals the government reduction of debt.
Now let us return to the Clinton years when the federal government was running the biggest budget surpluses the government has ever run. Everyone thought this was great because it meant that the government’s outstanding debt was being reduced. Clinton even went on TV and predicted that the budget surpluses would last for at least 15 years and that every dollar of government debt would be retired.
Everyone celebrated this accomplishment, and claimed the budget surplus was great for the economy.
In the middle of 2000, I wrote a contrary opinion (“Implications of a budget surplus at mid-year 2000, CFEPS Policy Note 2000/1). I made several arguments. First, I pointed out that the budget surplus meant by identity that the private sector was running a deficit. Households and firms were going ever farther into debt, and they were losing their net wealth of government bonds.
Second, I argued that this would eventually cause a recession because the private sector would become too indebted and thus would cut back spending. In fact, the economy went into recession within half a year.
Third, I argued that the budget surpluses would not last 15 years, as Clinton claimed. Indeed, I expected they would not last more than a couple of years. In fact, the budget turned around to large and growing deficits almost immediately as soon as the economy went into recession.
And of course we still have large budget deficits. No one talks any more about achieving budget surpluses this decade; almost everyone agrees that we will not see budget surpluses again in our lifetimes—if ever.
The question is whether the US government can run deficits forever. The answer is emphatically “yes”, and that it had better do so. If you look back to 1776, the federal budget has run a continuous deficit except for 7 short periods. The first 6 of those were followed by depressions—the last time was in 1929 which was followed by the Great Depression. The one exception was the Clinton budget surplus, which was followed (so far) only by a recession.
Why is that? By identity, budget surpluses suck income and wealth out of the private sector. This causes private spending to fall, leading to downsizing and unemployment. The only way around that is to run a trade or current account surplus.
The problem is that it is hard to see how the US can do that—in fact, our current account deficit is now rising toward 7% of GDP. All things equal, that means our budget deficit has to be even larger to allow our private sector to save. Given our current account balance, the budget deficit would have to reach 9% of GDP to allow our private sector to have a surplus of 2% of GDP.
I don’t want to give the impression that government deficits are always good, or that the bigger the deficit, the better. The point I am making is that we have to recognize the macro relations among the sectors.
If we say that a government deficit is burdening our future children with debt, we are ignoring the fact that this is offset by their saving and accumulation of financial wealth in the form of government debt. It is hard to see why households would be better off if they did not have that wealth.
If we say that the government can run budget surpluses for 15 years, what we are ignoring is that this means the private sector will have to run deficits for 15 years—going into debt that totals trillions of dollars in order to allow the government to retire its debt. Again it is hard to see why households would be better off if they owed more debt, just so that the government would owe them less.
There are other differences between the federal government and an individual household. The government is the issuer of our currency, while households are users of the currency. That makes a big difference, and one explored in many other CFEPS publications. However, the purpose of this particular note is to explain why we cannot aggregate up from the individual household situation to the economy as a whole. The US government’s situation is not in any way similar to that of a household because its deficit spending is exactly offset by private sector surpluses; its debt creates equivalent net financial wealth for the private sector.